What is HHC? The new Cannabinoid
Table of Contents
Brief Overview of the Topic
So what is HHC? Well to understand what HHC is, we first need to cover the topic of cannabis in this HHC cannabinoid review.
Cannabis is a plant that contains numerous compounds, including cannabinoids. These compounds have different effects on the human body and are being investigated for their potential therapeutic uses.
One of the lesser-known cannabinoids is hexahydrocannabinol (HHC). HHC is a psychoactive compound that’s structurally similar to THC, which is the primary psychoactive cannabinoid in cannabis.
HHC has been gaining attention among cannabis researchers and enthusiasts because it offers some unique benefits without some of the drawbacks associated with THC. While research on HHC is still limited, early studies suggest that it has potential therapeutic uses in treating various health conditions.
Explanation of and how it relates to cannabis
HHC, also known as cannabinolic cyclohexene, belongs to a family of cyclic terpenoids called cannabinoids. It’s chemically similar to THC but differs in its molecular structure by having a cyclohexene ring instead of a pyran ring found in THC. This structural difference can affect how HHC interacts with the body’s endocannabinoid system.
The endocannabinoid system (ECS) plays an essential role in regulating various physiological processes such as pain, mood, appetite, and sleep. Cannabinoids like THC and CBD interact with this system by binding to CB1 or CB2 receptors located throughout the body.
HHC also interacts with these receptors but has unique binding properties compared to other cannabinoids. This difference in binding affinity may explain why HHC produces slightly different effects than other cannabinoids such as THC or CBD.
The Potential Benefits of Using HCC over other Cannabinoids
While research on HCC is still limited compared to other more well-known cannabinoids like THC or CBD, early studies suggest that HCC may offer some potential therapeutic benefits without some of the drawbacks associated with THC. One of the significant benefits of using HCC is that it produces less psychoactive effects than THC.
This quality makes it attractive to those who want to use cannabis for its potential medicinal purposes without feeling “high.” Another potential benefit of HCC is that it may have fewer side effects. For example, studies suggest that HCC does not produce the same level of anxiety or paranoia associated with THC.
Additionally, research has shown a promising ability to reduce inflammation and alleviate pain in various conditions such as arthritis, multiple sclerosis, and neuropathic pain. Studies also suggest that it may help to reduce seizures in certain types of epilepsy.
More research is needed to fully understand the therapeutic benefits or risks associated with HHC use. However, these early studies suggest that this compound warrants further exploration as a potential medical treatment option for various health conditions.
What is Hexahydrocannabinol?
Hexahydrocannabinol (HHC) is a newly discovered compound found in cannabis that has gained attention for its potential therapeutic benefits. It is a cannabinoid, which means it interacts with the endocannabinoid system in the human body. The chemical structure of HHC is similar to that of THC, but there are some key differences between the two compounds.
Definition and Chemical Structure of HHC
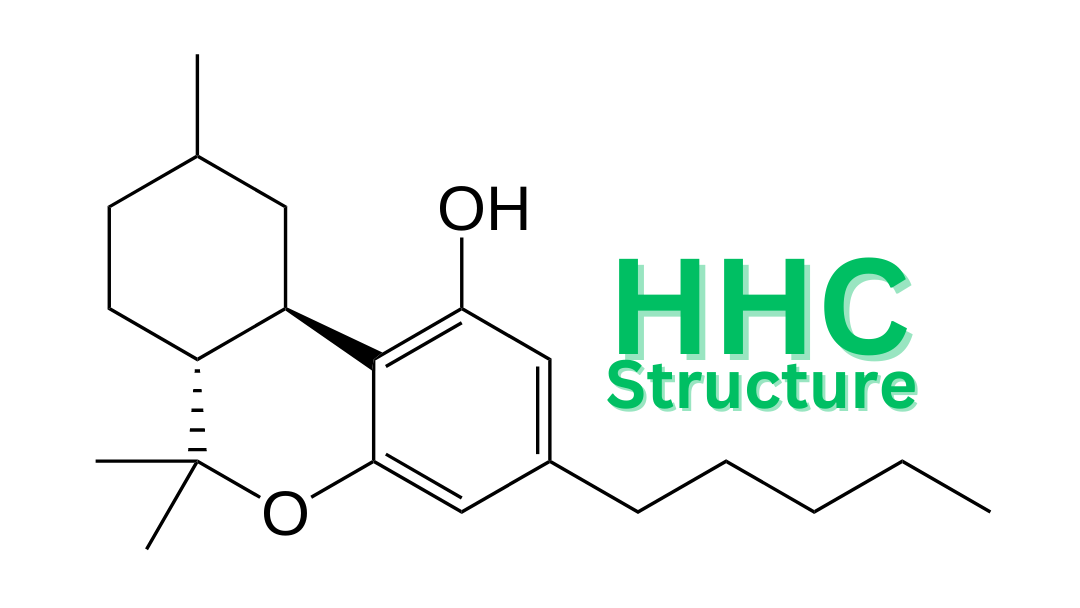
HHC is a cyclic cannabinoid that contains six rings of carbon atoms, hence its name “hexahydrocannabinol.” Its chemical formula is C21H34O2, which means it consists of 21 carbon atoms, 34 hydrogen atoms, and 2 oxygen atoms. The molecular weight of HHC is 318.5 g/mol. Compared to THC, HHC has an additional ring structure and lacks the double bond between carbon atoms in ring A. This difference in structure affects how the compound interacts with cannabinoid receptors in the body and could potentially lead to different effects compared to THC.
How it differs from THC and other cannabinoids
One significant difference between HHC and THC is their psychoactive properties. While THC is known for its intoxicating effects on the brain, research suggests that HHC may not have the same level of psychoactivity.
This makes it an interesting alternative for individuals who want to avoid feeling high while still experiencing potential therapeutic benefits. Another difference between these two cannabinoids lies in their origin within cannabis plants.
Unlike THC, which arises from cannabigerolic acid (CBGA), one precursor molecule responsible for producing various cannabinoids including CBD or CBC-HC (cannabichromene hexyl carbamate), HCC develops from another precursor known as cannabichromenic acid (CBCA). Research on other non-THC cannabinoids has shown that they could have unique therapeutic properties.
For example, cannabidiol (CBD) has been investigated for its potential anti-inflammatory, anti-anxiety, and antipsychotic effects. Similarly, HCC could possess therapeutic benefits that differ from THC or other cannabinoids.
Potential Benefits and Drawbacks of HHC Use
Initial studies suggest that HHC may have potential as an analgesic and anxiolytic agent. It may also help reduce inflammation in the body, making it a promising candidate for treating conditions such as arthritis or Crohn’s disease. While the research on HHC is still in its early stages, some drawbacks are associated with its use.
Due to the lack of regulation surrounding HHC production, it is essential to obtain products from reputable sources to ensure safety and quality control. Additionally, there is a need for more extensive research to understand the range of effects associated with using HHC.
As with any new compound or drug, there is always a possibility of unknown side effects that could emerge as more people start using it. Overall, despite limited research available at this time on HCC’s potential benefits and drawbacks, it has gained attention within the medical community as a promising alternative to THC with potential therapeutic benefits and fewer psychoactive effects.
History of HHC
Hexahydrocannabinol (HHC) is one of the lesser-known cannabinoids found in cannabis plants. Discovered in the 1940s, HHC was originally thought to be a precursor to THC, but later research showed that it is a unique compound with its own distinct chemical structure and effects.
Despite being discovered more than half a century ago, research on HHC has been limited compared to other cannabinoids like THC and CBD. The lack of research can be attributed to various factors such as legal restrictions and the relative uninterest of pharmaceutical companies in studying the therapeutic potential of minor cannabinoids.
Discovery and early research on HHC
The first studies on HHC were conducted by American chemist Roger Adams in the 1940s. Adams identified HCC as one of several compounds present in cannabis resin, and he noted that it had at least some psychoactive properties.
However, despite initial interest in studying this novel compound, subsequent research became scarce. This was partly due to difficulty isolating pure samples of HCC from cannabis resin; however, it is also likely that researchers were more interested in studying THC due to its greater abundance and well-known psychoactive effects.
Current state of research on HHC
Today, interest in researching minor cannabinoids such as HCC has increased due to growing realization that they may have therapeutic potential for treating a variety of medical conditions. However, compared to other cannabinoids like CBD or THC, there is still relatively little known about the potential benefits or drawbacks associated with consuming or using this compound. Some preliminary studies have suggested that hexahydrocannabinol may have anxiolytic (anti-anxiety) effects similar to those seen with CBD; however, further research will be needed before any definitive conclusions can be drawn regarding its therapeutic efficacy.
Is HHC Legal? Status and regulation of HHC
The legal status of HHC is currently unclear, as it is not specifically regulated under most existing cannabis laws. However, as with other minor cannabinoids, the legal situation may change in the future if more research is done and it shows potential therapeutic benefits.
In the meantime, users should exercise caution when consuming or using HCC, as there may be risks associated with using an untested compound. Additionally, users should be aware of any state or local regulations that may apply to the use of this compound.
Does HHC get you high? Effects of HHC on the Body
Hexahydrocannabinol (HHC) is a relatively new and understudied compound, making it difficult to determine its effects on the body with certainty. However, research thus far indicates that HHC may interact with the endocannabinoid system in a similar way to tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the primary psychoactive compound in cannabis. This interaction can lead to a range of effects on the body, including altered perception, mood changes, and potential therapeutic benefits. The simple answer is yes it can get you high but it is a different high to that of THC.
How HHC Interacts with the Endocannabinoid System
The endocannabinoid system is a network of receptors found throughout the body that are responsible for regulating various physiological processes such as pain sensation, appetite, and stress response. The two main receptors in this system are CB1 and CB2, which are primarily located in the brain and immune system respectively. When HHC interacts with these receptors, it can activate or inhibit various signaling pathways which lead to different effects on the body.
Some research suggests that HHC may be a partial agonist of both CB1 and CB2 receptors, meaning that it can bind to these receptors but does not fully activate them. This partial activation may contribute to some of the unique effects associated with HHC use.
Potential Therapeutic Uses for HHC
While research on HHC is still limited, preliminary findings suggest that it may have some potential therapeutic uses. For example, some studies have found that HCC has analgesic properties and can reduce pain levels in animal models.
Additionally, because of its ability to interact with certain neurotransmitters in the brain such as dopamine and serotonin, there is speculation that it could be used to treat anxiety or depression. However, more research is needed before any definitive conclusions can be drawn about these potential therapeutic uses for HHC.
HHC Effects: Risks Associated with Using HHC
As with any psychoactive substance, there are potential risks associated with using HHC. Some research has suggested that it may cause temporary cognitive impairments such as memory problems or difficulty concentrating.
Additionally, because of its similarity to THC, there is concern that it could lead to addiction or dependence if used regularly. Furthermore, because HHC is not yet widely available and regulated, there is a risk of contamination or adulteration in products containing this compound.
This could lead to unintended side effects or interactions with other substances. Overall, while the potential benefits and risks associated with using HHC are still largely unknown, continued research in this area may provide valuable insights into the therapeutic potential of this novel cannabinoid.
Methods of Consumption
Different Ways to Consume or Use HHC
HHC can be consumed in a variety of ways, similar to THC and other cannabinoids. Smoking is one of the most common methods, which involves heating the HHC and inhaling its vapors. Vaping is another popular option that heats the HHC at a lower temperature than smoking, producing less harmful toxins.
This method usually requires a vaporizer designed for cannabis concentrates. Edibles are also an option for consuming HHC.
These products come in various forms like gummies, chocolates, and baked goods infused with HHC oil or butter. The effects may take longer to set in but can last longer than smoking or vaping.
Tinctures and topicals are other alternatives that allow for precise dosing and easy application. Tinctures are liquid extracts that can be added to food or drinks while topicals are applied directly on the skin.
Is HHC Safe? Dosage Recommendations for Safe Use
Since HHC is a new cannabinoid without established research about its effects on the human body, there is no official recommended dosage yet. However, it’s important to start with small doses if you’re trying it for the first time. For smoking or vaping, experts suggest starting with one small inhale and waiting at least 10-15 minutes before taking another hit.
This allows you to see how your body reacts to the dose before consuming more. When it comes to edibles, always check the packaging for dosing instructions as they vary depending on product strength and serving size.
Keep in mind that edibles take longer to kick in compared to smoking or vaping because they need time to be digested by your body. In general, it’s best to start with lower doses until you find what works best for you without experiencing any adverse side effects such as paranoia or anxiety.
Conclusion
Hexahydrocannabinol (HHC) is a relatively unknown cannabinoid with potential therapeutic benefits. While research on HHC is still in its early stages, it has shown promise in treating conditions such as chronic pain and anxiety disorders. However, much more research is needed to fully understand the effects and potential risks associated with consuming HHC.
One of the key takeaways from this article is that HHC differs from other cannabinoids like THC and CBD in its chemical structure and effects on the body. As such, it should be approached with caution when considering use for medical or recreational purposes.
Looking forward, the research on HHC will undoubtedly continue to evolve as more studies are conducted and its potential benefits are better understood. While there may be some hurdles to overcome regarding legal status and regulation, there is hope that HHC could one day become an important tool for treating a range of health conditions.
Overall, while there is still much we don’t know about HHC, it is clear that this cannabinoid holds significant potential for those seeking alternative treatments for chronic pain or other health issues. As further research emerges, we will undoubtedly learn more about how best to use this compound to improve human health and well-being.
If you got this far, thank you for reading. If you would like to find out about some of the other cannabinoids, check out our other article on the subject here.



